06 Jul Metrics for Grant-Seeking By: Kellie Brungard, GPC
Posted at 18:00h
in Competency Two, Evaluation, Funding, Funding Opportunities, Kellie Brunguard, Organizational Development
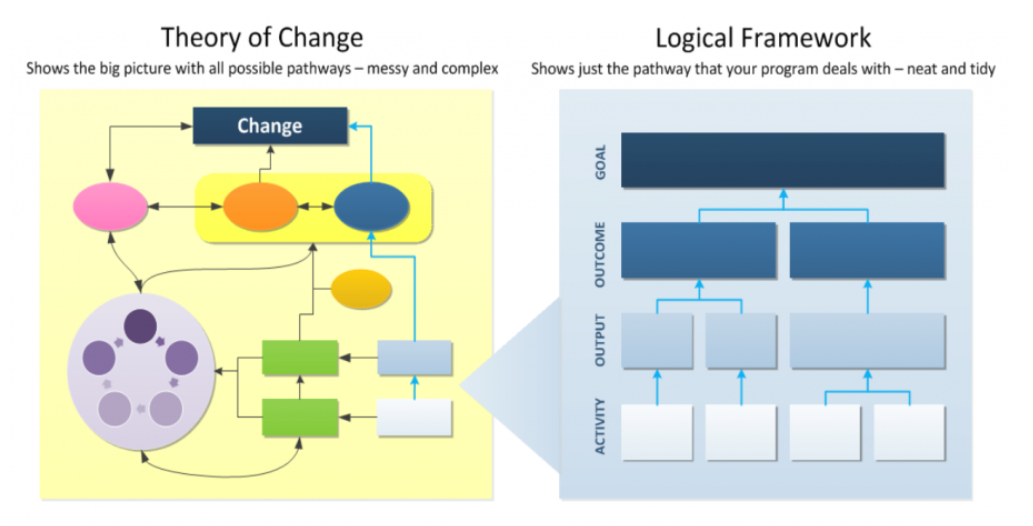
As a grant professional, are you asked to identify performance measurements for your organization or clients? Evaluating the performance of a grant department or grant professional is a nuanced task. Yet data helps leadership and the board of directors quantify the year-to-year success and progress toward department goals. All too often, an organization will set unrealistic goals without adequate resources or available opportunities or set unreasonable expectations for the number of applications an individual needs to submit. Looking at a “success rate” can fail to consider the organization's readiness, quality of program design, or ability to identify strong opportunities and stewardship. So, how can an organization effectively evaluate the performance of a grant department and set realistic goals? How can grant professionals articulate their skills and achievements to those who are data-minded?